Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 with carbon-ion microbeam
with carbon-ion microbeam坂下 哲哉; 鈴木 芳代; 浜田 信行*; 深本 花菜; 横田 裕一郎; 舟山 知夫; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
原子力機構(高崎研)のイオン照射研究施設(TIARA)には、AVFサイクロトロン加速器によって得られる高LET炭素イオンビームをマイクロビーム化し細胞等の生物試料に照射することが可能である。私たちは、多細胞生物である線虫の神経組織に、この炭素イオンマイクロビームを照射し神経系の機能である学習行動に影響が及ぶかどうかを検討してきた。これまでに、神経麻酔を施した線虫へのマイクロビーム照射実験から、神経機能を停止させた場合には、学習行動への影響が観られないことを確認した。また、ブロードビーム照射実験からは、学習過程の途中に炭素イオンを被ばくすると学習行動の変化が生じることを明らかにしている。そのため、学習過程の途中の生理的な状態が、放射線が線虫の学習行動を変化させるときに重要な鍵となることが示唆された。今後は、神経麻酔をしない状態の線虫に炭素イオンマイクロビームを照射する実験系を構築し、線虫の神経系の直接的な被ばくの影響を調べる予定である。
神谷 富裕; 及川 将一*; 佐藤 隆博; 柏木 啓次; 島田 博文*; 荒川 和夫; 遊佐 顕*; 中野 隆史*
no journal, ,
The high-precision carbon ion microsurgery is a technique to irradiate a minute tumor or a small part of disease deep inside of the body by a beam of high-energy carbon ion focused down to a width of 100  m to 5 mm and with a positional accuracy of less than 1 mm. This challenging technique had been planned to be introduced to one of the irradiation ports of heavy-ion irradiation facility of Gunma University Heavy Ion Medical Center (GHMC). The beam transport system of the (vertical) port for the development of this technique was designed based on an ion optical calculation code, TRANSPORT. Aiming at adjusting the system to range shift of the ion beam for therapy, basic concept of this ion optical system was telescopic, achromatic, and analyzable of the energy of ion beams. Details of the ion optical calculation for the system will be presented.
m to 5 mm and with a positional accuracy of less than 1 mm. This challenging technique had been planned to be introduced to one of the irradiation ports of heavy-ion irradiation facility of Gunma University Heavy Ion Medical Center (GHMC). The beam transport system of the (vertical) port for the development of this technique was designed based on an ion optical calculation code, TRANSPORT. Aiming at adjusting the system to range shift of the ion beam for therapy, basic concept of this ion optical system was telescopic, achromatic, and analyzable of the energy of ion beams. Details of the ion optical calculation for the system will be presented.
舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; 深本 花菜; 横田 裕一郎; 鈴木 芳代; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
原子力機構では、高崎量子応用研究所TIARAにおいて、生物試料照射用マイクロビーム装置の開発を行ってきた。当該装置は、5 m径の重イオンビームで細胞を一つ一つ照準して照射することができる。このマイクロビーム装置を利用して、動植物の培養細胞を始め、カイコ初期胚・幼虫,シロイヌナズナ根組織,線虫などのさまざまな生物材料に対する照射実験が行われ、放射線生物学領域のみならず、生理学,発生生物学,神経生物学など、幅広い領域の研究に貢献してきた。
m径の重イオンビームで細胞を一つ一つ照準して照射することができる。このマイクロビーム装置を利用して、動植物の培養細胞を始め、カイコ初期胚・幼虫,シロイヌナズナ根組織,線虫などのさまざまな生物材料に対する照射実験が行われ、放射線生物学領域のみならず、生理学,発生生物学,神経生物学など、幅広い領域の研究に貢献してきた。
横田 裕一郎; 舟山 知夫; 浜田 信行*; 坂下 哲哉; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
重粒子線がん治療が実施あるいは計画されている。高LETの重イオンは、低LETの光子放射線と比べて、正常組織や腫瘍に及ぼす効果が大きい。本研究では、重イオンの生物効果が大きいメカニズムを探る目的で、ヒト正常線維芽細胞におけるイオンビームの細胞致死効果を調べた。ヒト二倍体正常線維芽細胞を高密度単層培養した後、 線(LETは0.2keV/
線(LETは0.2keV/ m),陽子(同2.8keV/
m),陽子(同2.8keV/ m),ヘリウム(同17keV/
m),ヘリウム(同17keV/ m),炭素(同70と110keV/
m),炭素(同70と110keV/ m),ネオン(同310と430keV/
m),ネオン(同310と430keV/ m)及びアルゴン(同1320と1530keV/
m)及びアルゴン(同1320と1530keV/ m)イオンを照射した。それぞれの放射線の10%生存線量は、4.3Gy, 3.2Gy, 2.4Gy, 1.0Gy, 1.4から1.6Gy及び3.7から5.0Gyだった。10%生存線量に基づく生物学的効果比は70及び110keV/
m)イオンを照射した。それぞれの放射線の10%生存線量は、4.3Gy, 3.2Gy, 2.4Gy, 1.0Gy, 1.4から1.6Gy及び3.7から5.0Gyだった。10%生存線量に基づく生物学的効果比は70及び110keV/ mの炭素イオンで、4.3の最大値に達した。この結果は、線量あたりの細胞致死効果が、炭素イオンでは
mの炭素イオンで、4.3の最大値に達した。この結果は、線量あたりの細胞致死効果が、炭素イオンでは 線と比べて4倍大きいことを示した。
線と比べて4倍大きいことを示した。
河地 有木; 渡邉 茂樹; 藤巻 秀; 石岡 典子; 佐藤 隆博; 神谷 富裕; 荒川 和夫; 渡辺 伸*; 武田 伸一郎*; 石川 真之介*; et al.
no journal, ,
The Compton camera is a next-generation in vivo imaging system. In order to achieve accurate Compton imaging, it is necessary to develop technologies that can be used to detect the Compton scattering in the camera and estimate the direction of a incoming  -ray produced by a radiation source. These techniques will be different from the methods used in PET and SPECT to detect the
-ray produced by a radiation source. These techniques will be different from the methods used in PET and SPECT to detect the  -ray with the coincidence of two points and with the physical collimation. We have developed a prototype Compton camera for in vivo imaging by using semiconductor imaging devices, which has been proved to be successful techniques for the an observation of high-energy astrophysical phenomena. In this camera, double-sided Si strip detectors (DSSDs) serve as scatterers and CdTe pixel detectors serve as absorbers. In this paper, we present some images acquired with the Compton camera; we have also acquired images of radioisotopes in a phantom, which reveal certain characteristic distributions of efficiencies and spatial resolutions.
-ray with the coincidence of two points and with the physical collimation. We have developed a prototype Compton camera for in vivo imaging by using semiconductor imaging devices, which has been proved to be successful techniques for the an observation of high-energy astrophysical phenomena. In this camera, double-sided Si strip detectors (DSSDs) serve as scatterers and CdTe pixel detectors serve as absorbers. In this paper, we present some images acquired with the Compton camera; we have also acquired images of radioisotopes in a phantom, which reveal certain characteristic distributions of efficiencies and spatial resolutions.
山口 充孝*; 荒川 和夫; 青野 博之*; 石川 真之介*; 神谷 富裕; 河地 有木; 小高 裕和*; 櫻井 英幸*; 佐藤 隆博; 島田 博文*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed a prototype of Compton camera using Si/CdTe semiconductors for medical imaging. In a Compton camera, employing the imaging semiconductors as the component of the Compton camera, with their good energy and position resolution, improves angular resolution and hence sensitivity. Moreover, for the supposed energy range of  rays, from several tens keV to a few MeV, silicon is suitable for the scatter of Compton camera since the photo absorption cross section of Si is small and the Compton cross-section is relatively large because of the small atomic number. On the other hand, CdTe is suitable for the absorbers because of its high photo-absorption efficiency for
rays, from several tens keV to a few MeV, silicon is suitable for the scatter of Compton camera since the photo absorption cross section of Si is small and the Compton cross-section is relatively large because of the small atomic number. On the other hand, CdTe is suitable for the absorbers because of its high photo-absorption efficiency for  rays of this energy region, due to the large atomic numbers. In this presentation we will summarize the basic principle and performance of the Si/CdTe Compton camera for medical imaging.
rays of this energy region, due to the large atomic numbers. In this presentation we will summarize the basic principle and performance of the Si/CdTe Compton camera for medical imaging.
山口 充孝*; 河地 有木; 渡辺 伸*; 小高 裕和*; 武田 伸一郎*; 石川 真之介*; 青野 博之*; 高橋 忠幸*; 荒川 和夫; 中野 隆史*
no journal, ,
We evaluated the position resolutions of single- and double-head Compton camera by using Monte Carlo simulation. A  -ray source was placed at the origin of rectangular coordinates. For single-head camera, one head was placed as its center axis was corresponding to the z-axis. For double-head camera, two heads were placed as those center axes were corresponding to the z- and y-axis, respectively. Monte Carlo simulations were performed by using the Geant4 toolkit on ANL PLUS framework. The energy of
-ray source was placed at the origin of rectangular coordinates. For single-head camera, one head was placed as its center axis was corresponding to the z-axis. For double-head camera, two heads were placed as those center axes were corresponding to the z- and y-axis, respectively. Monte Carlo simulations were performed by using the Geant4 toolkit on ANL PLUS framework. The energy of  rays was set at 364.5 keV, which correspond to radiation of iodine-131. After these simulations, two hit Compton event was selected. And then back-projection and image reconstruction were performed in 3D-space. Image reconstructions were performed by using the List-Mode Most- Likelihood Expectation-Maximizing, LM-ML-EM, algorithm. Consequently, the position resolution (FWHM) of the z-axis was about 4.4 mm for double-head camera whereas about 15 mm for single-head camera. These values are consistent with the values roughly estimated by using angular resolution measure (ARM). These results indicate that the position resolution is improved and clear 3D-image is taken by using multi-head Compton camera.
rays was set at 364.5 keV, which correspond to radiation of iodine-131. After these simulations, two hit Compton event was selected. And then back-projection and image reconstruction were performed in 3D-space. Image reconstructions were performed by using the List-Mode Most- Likelihood Expectation-Maximizing, LM-ML-EM, algorithm. Consequently, the position resolution (FWHM) of the z-axis was about 4.4 mm for double-head camera whereas about 15 mm for single-head camera. These values are consistent with the values roughly estimated by using angular resolution measure (ARM). These results indicate that the position resolution is improved and clear 3D-image is taken by using multi-head Compton camera.
吉田 由香里*; 島田 博文*; 河地 有木; 武田 伸一郎*; 石川 真之介*; 青野 博之*; 鈴木 義行*; 櫻井 英幸*; 渡辺 伸*; 山口 充孝*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed a prototype Compton camera for medical imaging by using Si/CdTe semiconductor imaging devices. The high detection efficiency for  -rays produced by radiation source in the medical imaging devices will improve quality of diagnostic radiological images using radiopharmaceuticals. The Si/CdTe Compton camera is a next-generation medical imaging device because it has good energy and position resolution, and high detection efficiency for
-rays produced by radiation source in the medical imaging devices will improve quality of diagnostic radiological images using radiopharmaceuticals. The Si/CdTe Compton camera is a next-generation medical imaging device because it has good energy and position resolution, and high detection efficiency for  -rays. Moreover, it can be used not only to detect the
-rays. Moreover, it can be used not only to detect the  -rays produced by single radiation source, but also to detect the
-rays produced by single radiation source, but also to detect the  -rays produced by multiple radiation sources. To evaluate the performance of the Si/CdTe Compton camera for medical imaging, we made an experiment of in vivo by using rat and plural radiopharmaceutical.
-rays produced by multiple radiation sources. To evaluate the performance of the Si/CdTe Compton camera for medical imaging, we made an experiment of in vivo by using rat and plural radiopharmaceutical.
鈴木 義行*; 吉田 由香里*; 島田 博文*; 加藤 弘之*; 櫻井 英幸*; 河地 有木; 武田 伸一郎*; 石川 真之介*; 青野 博之*; 渡辺 伸*; et al.
no journal, ,
本研究は、現在開発を進めているSi/CdTeコンプトンカメラの医療への応用について検討したものである。本報告では、これまで開発を進めてきたプロトタイプ機を用い、ラットに投与した3核種( In,
In,  I,
I,  Cu)のイメージング及びファントム実験結果について述べる。さらに、多核種同時イメージングによる新たな診断法及び微小な病変部位の精密診断法について述べるとともに、照射した重粒子イオンの体内位置のリアルタイムモニターによるがん治療の高精度化への期待と今後の臨床利用までの研究計画について述べる。
Cu)のイメージング及びファントム実験結果について述べる。さらに、多核種同時イメージングによる新たな診断法及び微小な病変部位の精密診断法について述べるとともに、照射した重粒子イオンの体内位置のリアルタイムモニターによるがん治療の高精度化への期待と今後の臨床利用までの研究計画について述べる。
 Br-
Br-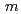 -bromobenzylgianidine (
-bromobenzylgianidine ( Br-MBBG)
Br-MBBG)渡邉 茂樹; 花岡 宏史*; Liang, J. X.; 飯田 靖彦*; 遠藤 啓吾*; 石岡 典子
no journal, ,
 Br (t
Br (t = 16.2 h,
= 16.2 h, 
 = 57%, EC = 43%) has intermediated half-life and may have great potentials as radionuclide for positron emission tomography (PET). We have produced
= 57%, EC = 43%) has intermediated half-life and may have great potentials as radionuclide for positron emission tomography (PET). We have produced  Br via the
Br via the  Se(p,n)
Se(p,n) Br reaction using Cu
Br reaction using Cu
 Se target, and also have interest in bromine labeled radiopharmaceuticals. Radioiodine labeled
Se target, and also have interest in bromine labeled radiopharmaceuticals. Radioiodine labeled 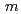 -iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) such as [
-iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) such as [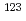 I] or [
I] or [ I]-MIBG have been widely employed for imaging of myocardial function and neuroendcrine tumor with single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). PET is superior in quantitative measurement to SPECT, thus positron emitter
I]-MIBG have been widely employed for imaging of myocardial function and neuroendcrine tumor with single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). PET is superior in quantitative measurement to SPECT, thus positron emitter  Br-labeled MIBG can be expected to employ as a novel imaging reagent for PET. In this study, we synthesized
Br-labeled MIBG can be expected to employ as a novel imaging reagent for PET. In this study, we synthesized  Br labeled meta-bromobenzylguanidine (
Br labeled meta-bromobenzylguanidine ( Br-MBBG) for tumor imaging by PET to evaluated stability in serum and biodistribution of
Br-MBBG) for tumor imaging by PET to evaluated stability in serum and biodistribution of  Br-MBBG using normal mice.
Br-MBBG using normal mice.
飯田 靖彦*; 花岡 宏史*; 吉岡 弘樹*; 高柳 恵美*; 渡邉 茂樹; 石岡 典子; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; Paudyal, P.*; 樋口 徹也*; et al.
no journal, ,
Some new radionuclides would be useful for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Our project is to prepare these radionuclides, to apply them to many radiopharmaceuticals and to investigate usefullness of those new radiopharmaceuticals. Radio immuno therapy (RIT) is one of the most promising treatments for cancer therapy. And assessment of radiation dose to both tumor and normal tissues is very important to RIT. PET can estimate radiation dose directly, but general positron emittors don't suit for labeling of antibody because of their short half-lives.  Cu and
Cu and  Br have appropriate properties (
Br have appropriate properties ( Cu: T
Cu: T = 12.7 hr,
= 12.7 hr,  Br: T
Br: T = 16.1 hr) and they may have great potentials for immuno-PET. We have synthesized
= 16.1 hr) and they may have great potentials for immuno-PET. We have synthesized  Cu or
Cu or  Br labeled monoclonal antibody and evaluated potentials for in vivo quantitative evaluation of RIT. And we synthesized
Br labeled monoclonal antibody and evaluated potentials for in vivo quantitative evaluation of RIT. And we synthesized  Br labeled glucose (
Br labeled glucose ( BrDG). We evaluated its utility for tumor diagnosis. These new radiopharmaceuticals are very useful for cancer diagnosis and therapy. We will develop various radiopharmaceuticals labeled with these new radionuclides and apply them to clinical medicine in future.
BrDG). We evaluated its utility for tumor diagnosis. These new radiopharmaceuticals are very useful for cancer diagnosis and therapy. We will develop various radiopharmaceuticals labeled with these new radionuclides and apply them to clinical medicine in future.